GABE -- The System Control, I/O, and Sound Chip
"GABE" is the name of the system controller chip of the C256 Foenix RevC board, and performs several functions including system bus management, math coprocessing, I/O, and sound.
The RevB version of the C256 had two chips "Gavin" and "Beatrix" that were combined into a single master chip called "GABE".
GABE has several key functions:
- System start up
- Debug interface control and bus mastering
- I/O interfacing
- Math coprocessor
- Sound chip interfacing and emulation
GABE System Startup Process
When the C256 Foenix powers up, GABE takes control and coordinates the startup process.
It first copies the flash data out of flash and into system RAM, starting at bank $38 on the FMX ($18 on the RevB).
GABE also copies the first bank of flash data down to bank $00 of system RAM
before control is given to the CPU and the CPU's RESET is triggered.
This process ensures that the kernel, hardware vectors, and interrupt handlers are all in place prior to the CPU
taking control and resetting the first time on power up.
The mapping of flash memory locations to system RAM is thus:
| Flash Range |
RAM Range
|
| $F8:0000...$FF:FFFF |
$38:0000...$3F:FFFF
|
| $F8:0000...$F8:FFFF |
$00:0000...$00:FFFF
|
GABE Integer Math Coprocessor ($00:0100 – $00:012B)
GABE provides an easy to use integer math coprocessor in the form of two 16-multipliers (one signed, one unsigned),
two 16-bit dividers (one signed, one unsigned), and a single 32-bit adder. Using the coprocessor is straight-forward:
the operands are written to the correct registers, and the result is read from the output registers. The operations
are all performed within a single CPU clock cycle, so no waiting is required.
| Start Address
|
End Address
|
Register Name
|
Additional Info
|
| $00:0100 |
$00:0101 |
UNSIGNED_MULT_A |
A operand for unsigned multiplication (16-bit)
|
| $00:0102 |
$00:0103 |
UNSIGNED_MULT_B |
B operand for unsigned multiplication (16-bit)
|
| $00:0104 |
$00:0107 |
UNSIGNED_MULT_RESULT |
Result for unsigned multiplication (32-bit)
|
| $00:0108 |
$00:0109 |
SIGNED_MULT_A |
A operand for signed multiplication (16-bit)
|
| $00:010A |
$00:010B |
SIGNED_MULT_B |
B operand for signed multiplication (16-bit)
|
| $00:010C |
$00:010F |
SIGNED_MULT_RESULT |
Result for signed multiplication (32-bit)
|
| $00:0110 |
$00:0111 |
UNSIGNED_DIV_DEM |
Denominator for unsigned division (16-bit)
|
| $00:0112 |
$00:0113 |
UNSIGNED_DIV_NUM |
Numerator for unsigned division (16-bit)
|
| $00:0114 |
$00:0115 |
UNSIGNED_DIV_QUO |
Quotient for unsigned division (16-bit)
|
| $00:0116 |
$00:0117 |
UNSIGNED_DIV_REM |
Remainder for unsigned division (16-bit)
|
| $00:0118 |
$00:0119 |
SIGNED_DIV_DEM |
Denominator for signed division (16-bit)
|
| $00:011A |
$00:011B |
SIGNED_DIV_NUM |
Numerator for signed division (16-bit)
|
| $00:011C |
$00:011D |
SIGNED_DIV_QUO |
Quotient for signed division (16-bit)
|
| $00:011E |
$00:011F |
SIGNED_DIV_REM |
Remainder for signed division (16-bit)
|
| $00:0120 |
$00:0123 |
ADDER32_A |
A operand for 32-bit addition (32-bits)
|
| $00:0124 |
$00:0127 |
ADDER32_B |
B operand for 32-bit addition (32-bits)
|
| $00:0128 |
$00:012B |
ADDER32_R |
Result of 32-bit addition (32-bits)
|
GABE Floating Point Math Coprocessor ($AF:E200 – AFE20F)
GABE provides a floating point math coprocessor, providing addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division for 32-bit floating point numbers.
Additionally, the coprocessor allows for conversion between a fixed point format and 32-bit IEEE 754 floating point format.
The floating point coprocessor is a little more complex than the integer coprocessor, with each math unit having input multiplexers that control
where the inputs come from, and with the output registers having their own multiplexer. Finally, the output of the multiplier and divider units
can be used directly as inputs to the adder/subtracter.
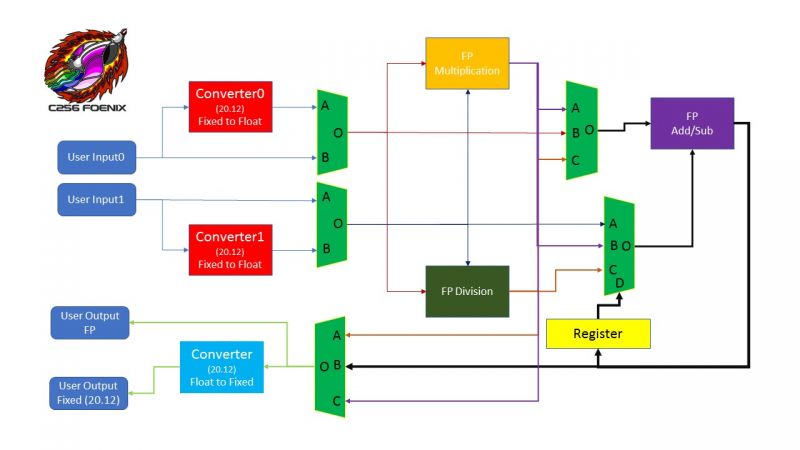
| Start Address |
End Address |
Register Name |
Additional Information
|
| $AF:E200 |
|
FP_MATH_CTRL0 |
Controls input multiplexers, Adder function, and Adder multiplexers
|
| $AF:E201 |
|
FP_MATH_CTRL1 |
Controls output multiplexers
|
| $AF:E202 |
|
FP_MATH_CTRL2 |
Unused: reserved
|
| $AF:E203 |
|
FP_MATH_CTRL3 |
Unused: reserved
|
| $AF:E204 |
|
FP_MATH_MULT_STAT |
Status of the multiplier
|
| $AF:E205 |
|
FP_MATH_DIV_STAT |
Status of the divider
|
| $AF:E206 |
|
FP_MATH_ADD_STAT |
Status of the adder/subtracter
|
| $AF:E207 |
|
FP_MATH_CONV_STAT |
Status of the converters
|
| $AF:E208 |
$AF:E20B |
FP_MATH_INPUT0 |
Input 0 (write only)
|
| $AF:E20C |
$AF:E20F |
FP_MATH_INPUT1 |
Input 1 (write only)
|
| $AF:E208 |
$AF:E20B |
FP_MATH_OUTPUT_FP |
Result in IEEE 754 format (read only)
|
| $AF:E20C |
$AF:E20F |
FP_MATH_OUTPUT_FIXED |
Result in 20.12 fixed point format (read only)
|
GABE Register FP_MATH_CTRL0 ($AF:E200)
| 7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0
|
| FP_MATH_CTRL0_ADD_IN1_MUX |
FP_MATH_CTRL0_ADD_IN0_MUX |
FP_MATH_CTRL0_ADD_SUB |
|
FP_MATH_CTRL0_INPUT1_MUX |
FP_MATH_CTRL0_INPUT0_MUX
|
- FP_MATH_CTRL0_INPUT0_MUX
- If 0, Input0 is assumed to be in IEEE format. If 1, it is assumed to be in 20.12 fixed point format and will be converted to IEEE.
- FP_MATH_CTRL0_INPUT1_MUX
- If 0, Input1 is assumed to be in IEEE format. If 1, it is assumed to be in 20.12 fixed point format and will be converted to IEEE.
- FP_MATH_CTRL0_ADD_SUB
- If 0, the adder will perform a subtract operation. If 1, it will perform an addition.
- FP_MATH_CTRL0_ADD_IN0_MUX
- Selects the source for input 0 of the adder unit.
- FP_MATH_CTRL0_ADD_IN1_MUX
- Selects the source for input 1 of the adder unit.
Adder Source Selector Codes
| Control Bits |
Input
|
| 00 |
Input 0
|
| 01 |
Input 1
|
| 10 |
Output of the multiplier
|
| 11 |
Output of the divider
|
GABE Register FP_MATH_CTRL1 ($AF:E201)
| 7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0
|
|
FP_MATH_CTRL1_OUTPUT_MUX0
|
- FP_MATH_CTRL1_OUTPUT_MUX0
- Selects which functional block provides the output result:
Result Source Selector Codes
| Control Bits |
Output Source
|
| 00 |
Result of multiplier is the routed to the output registers
|
| 01 |
Result of divider is the routed to the output registers
|
| 10 |
Result of adder is the routed to the output registers
|
| 11 |
1.0 is routed to the output registers
|
GABE Registers: FP Status Registers ($AF:E204 – $AF:E207)
These registers contain the status flags for the various functional units. The status flags are all roughly similar across the four units:
Status Codes
| Code |
Meaning
|
| $01 |
Result was not a number (NAN)
|
| $02 |
Overflow
|
| $04 |
Underflow
|
| $08 |
Result was 0.0
|
| $10 |
Division by 0.0 was attempted
|
GABE Interrupt Control Registers ($00:0140 – $00:014B)
There are four types of interrupt control register that GABE provides: pending, polarity, edge detection, and mask.
Each interrupt that is supported has a bit position in each of the 24 or 32 bits provided by the register types.
- Pending
- The pending registers indicate if an interrupt of a particular type has been triggered and needs processing. An interrupt handler should also write to this register to clear the pending flag, once the interrupt has been processed.
- Polarity
- This register indicates if the interrupt is triggered by a high or low signal on the input to GABE.
- Edge
- This register indicates if the interrupt is triggered by an transition (edge) or by a high or low value.
- Mask
- This register indicates if the associated interrupt will trigger an IRQ to the processor. Interrupt signals with a mask bit of 0 will be ignored, while those with a mask bit of 1 will trigger an interrupt to the CPU.
| Start
|
Register Description
|
Additional Info
|
| $00:0140 |
INT_PENDING_REG0 |
Interrupt pending #0
|
| $00:0141 |
INT_PENDING_REG1 |
Interrupt pending #1
|
| $00:0142 |
INT_PENDING_REG2 |
Interrupt pending #2
|
| $00:0143 |
INT_PENDING_REG3 |
Interrupt pending #3---FMX Model only
|
| $00:0144 |
INT_POL_REG0 |
Interrupt polarity #0
|
| $00:0145 |
INT_POL_REG1 |
Interrupt polarity #1
|
| $00:0146 |
INT_POL_REG2 |
Interrupt polarity #2
|
| $00:0147 |
INT_POL_REG3 |
Interrupt polarity #3---FMX Model only
|
| $00:0148 |
INT_EDGE_REG0 |
Enable Edge Detection #0
|
| $00:0149 |
INT_EDGE_REG1 |
Enable Edge Detection #1
|
| $00:014A |
INT_EDGE_REG2 |
Enable Edge Detection #2
|
| $00:014B |
INT_EDGE_REG3 |
Enable Edge Detection #3---FMX Model only
|
| $00:0148 |
INT_MASK_REG0 |
Enable Interrupt #0
|
| $00:0149 |
INT_MASK_REG1 |
Enable Interrupt #1
|
| $00:014A |
INT_MASK_REG2 |
Enable Interrupt #2
|
| $00:014B |
INT_MASK_REG3 |
Enable Interrupt #3---FMX Model only
|
There are several interrupts the GABE can handle, distributed over four blocks:
| Block |
Bit |
Name |
Function
|
| 0 |
$01 |
FNX0_INT00_SOF |
Start of Frame @60Hz
|
| 0 |
$02 |
FNX0_INT01_SOL |
Start of Line (programmable)
|
| 0 |
$04 |
FNX0_INT02_TMR0 |
Timer 0
|
| 0 |
$08 |
FNX0_INT03_TMR1 |
Timer 1
|
| 0 |
$10 |
FNX0_INT04_TMR2 |
Timer 2
|
| 0 |
$20 |
FNX0_INT05_RTC |
Real Time Clock
|
| 0 |
$40 |
FNX0_INT06_FCC |
Floppy Drive Controller
|
| 0 |
$80 |
FNX0_INT07_MOUSE |
Mouse Interrupt (INT12 in SuperIO IOspace)
|
| 1 |
$01 |
FNX1_INT00_KBD |
Keyboard Interrupt
|
| 1 |
$02 |
FNX1_INT01_SC0 |
VICKY_II (INT2) Sprite 2 Sprite Collision
|
| 1 |
$04 |
FNX1_INT02_SC1 |
VICKY_II (INT3) Sprite 2 Tiles Collision
|
| 1 |
$08 |
FNX1_INT03_COM2 |
Serial Port 2 (Internal)
|
| 1 |
$10 |
FNX1_INT04_COM1 |
Serial Port 1 (External)
|
| 1 |
$20 |
FNX1_INT05_MPU401 |
Midi Controller Interrupt
|
| 1 |
$40 |
FNX1_INT06_LPT |
Parallel Port
|
| 1 |
$80 |
FNX1_INT07_SDCARD |
SD Card Controller Interrupt (CH376S, if present)
|
| 2 |
$01 |
FNX2_INT00_OPL3 |
OPL3
|
| 2 |
$02 |
FNX2_INT01_GABE_INT0 |
GABE (INT0) - TBD
|
| 2 |
$04 |
FNX2_INT02_GABE_INT1 |
GABE (INT1) - TBD
|
| 2 |
$08 |
FNX2_INT03_SDMA |
VICKY_II (INT4)
|
| 2 |
$10 |
FNX2_INT04_VDMA |
VICKY_II (INT5) -- Vicky DMA completion
|
| 2 |
$20 |
FNX2_INT05_GABE_INT2 |
GABE (INT2) - TBD
|
| 2 |
$40 |
FNX2_INT06_EXT |
External Expansion
|
| 2 |
$80 |
FNX2_INT07_SDCARD_INS |
SDCARD Insertion
|
| 3 |
$01 |
FNX3_INT00_OPN2 |
OPN2
|
| 3 |
$02 |
FNX3_INT01_OPM |
OPM
|
| 3 |
$04 |
FNX3_INT02_IDE |
HDD IDE Interrupt
|
| 3 |
$08 |
FNX3_INT03_TBD |
TBD
|
| 3 |
$10 |
FNX3_INT04_TBD |
TBD
|
| 3 |
$20 |
FNX3_INT05_TBD |
TBD
|
| 3 |
$40 |
FNX3_INT06_TBD |
TBD
|
| 3 |
$80 |
FNX3_INT07_TBD |
TBD
|
GABE SID Emulation ($AF:E400 – $AF:E41F)
GABE emulates the SID sound chip. Currently, the FMX provides one SID unit.
Although the real SID chip provides analog to digital conversion for two
potentiometer inputs for paddles, the C256's paddle inputs are provided through
a different chip, so the POT registers listed below are not useful.
For complete information on how to use these registers, please consult documentation
on the SID chips.
All registers are write-only, except where noted otherwise.
| Start Address |
End Address |
Register Name |
Additional Information
|
| $AF:E400 |
$AF:E401 |
SID0_V1_FREQ |
SID0 V1 Frequency (16-bits)
|
| $AF:E402 |
$AF:E403 |
SID0_V1_PW |
SID0 V1 Pulse Width (12-bits)
|
| $AF:E404 |
|
SID0_V1_CTRL |
SID0 V1 Control (8-bits)
|
| $AF:E405 |
|
SID0_V1_ATCK_DECY |
SID0 V1 Attack/Decay (8-bits)
|
| $AF:E406 |
|
SID0_V1_SSTN_RLSE |
SID0 V1 Sustain/Release (8-bits)
|
| $AF:E407 |
$AF:E408 |
SID0_V2_FREQ |
SID0 V2 Frequency (16-bits)
|
| $AF:E409 |
$AF:E40A |
SID0_V2_PW |
SID0 V2 Pulse Width (12-bits)
|
| $AF:E40B |
|
SID0_V2_CTRL |
SID0 V2 Control (8-bits)
|
| $AF:E40C |
|
SID0_V2_ATCK_DECY |
SID0 V2 Attack/Decay (8-bits)
|
| $AF:E40D |
|
SID0_V2_SSTN_RLSE |
SID0 V2 Sustain/Release (8-bits)
|
| $AF:E40E |
$AF:E40F |
SID0_V3_FREQ |
SID0 V3 Frequency (16-bits)
|
| $AF:E410 |
$AF:E411 |
SID0_V3_PW |
SID0 V3 Pulse Width (12-bits)
|
| $AF:E412 |
|
SID0_V3_CTRL |
SID0 V3 Control (8-bits)
|
| $AF:E413 |
|
SID0_V3_ATCK_DECY |
SID0 V3 Attack/Decay (8-bits)
|
| $AF:E414 |
|
SID0_V3_SSTN_RLSE |
SID0 V3 Sustain/Release (8-bits)
|
| $AF:E415 |
|
SID0_FC_LO |
SID0 Filter Frequency LOW (3 bits)
|
| $AF:E416 |
|
SID0_FC_HI |
SID0 Filter Frequency HIGH (8 bits)
|
| $AF:E417 |
|
SID0_RES_FILT |
SID0 Resonance / Filter (8-bits)
|
| $AF:E418 |
|
SID0_MODE_VOL |
SID0 Mode / Volume (8-bits)
|
| $AF:E419 |
|
SID0_POT_X |
SID0 POT X (Read only, C256 - NOT USED)
|
| $AF:E41A |
|
SID0_POT_Y |
SID0 POT Y (Read only, C256 - NOT USED)
|
| $AF:E41B |
|
SID0_OSC3_RND |
SID0 OSC3 / RANDOM (Read only, 8-bits)
|
| $AF:E41C |
|
SID0_ENV3 |
SID0 ENV3 (Read only, 8-bits)
|
GABE Control Registers ($AF:E880 – $AF:E887)
| Start Address
|
Ending Address
|
Register Description
|
Additional Info
|
| $AF:E880 |
|
GABE_MSTR_CTRL
|
| $AF:E881 |
|
Reserved
|
| $AF:E882 |
|
GABE_RST_AUTH0 |
Must Contain the BYTE $AD for Reset to Activate
|
| $AF:E883 |
|
GABE_RST_AUTH1 |
Must Contain the BYTE $DE for Reset to Activate
|
| $AF:E884 |
$AF:E885 |
GABE_RNG_DATASEED |
On read: 16-bit random data. On write, set 16-bit RNG seed.
|
| $AF:E886 |
|
GABE_RNG_STATCTRL |
On read: 8-bit status. On write: 8-bit control
|
| $AF:E887 |
|
GABE_SYS_STAT |
8-bit system status
|
GABE Master Control Register ($AF:E880)
| 7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0
|
| GABE_CTRL_WRM_RST |
|
|
GABE_CTRL_BUZZER |
|
|
GABE_CTRL_SDC_LED |
GABE_CTRL_PWR_LED
|
- GABE_CTRL_PWR_LED
- Turns the power LED (next to the reset button) on or off.
- GABE_CTRL_SDC_LED
- Turns the SDC activity LED (next to the SDC slot) on or off.
- GABE_CTRL_BUZZER
- Turns the built-in piezo buzzer on or off.
- GABE_CTRL_WRM_RST
- Triggers a warm reset of the board (GABE_RST_AUTH0 must be set to $AD and GABE_RST_AUTH1 to $DE in order to trigger the reset).
GABE System Status Register ($AF:E887)
| 7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0
|
| GABE_SYS_STAT_CPUX |
GABE_SYS_STAT_CPUA |
|
|
GABE_SYS_STAT_EXP |
|
GABE_SYS_STAT_MID1 |
GABE_SYS_STAT_MID0
|
- GABE_SYS_STAT_CPUX
- Indicates if the CPU's index registers are 8-bits or 16-bits wide.
- GABE_SYS_STAT_CPUA
- Indicates if the CPU's accumulator is 8-bits or 16-bits wide.
- GABE_SYS_STAT_EXP
- Indicates if the and expansion card is present (0).
- GABE_SYS_STAT_MID1 and GABE_SYS_STAT_MID0
- These two bits show the machine ID:
| GABE_SYS_STAT_MID1 |
GABE_SYS_STAT_MID0 |
Machine
|
| 0 |
0 |
FMX - Development Platform
|
| 0 |
1 |
C256 Foenix - Dev Platform
|
| 1 |
0 |
C256 Foenix - User Version (65C816)
|
| 1 |
1 |
Reserved
|
